
- Drive format that works for mac and windows fat how to#
- Drive format that works for mac and windows fat windows#
Drive format that works for mac and windows fat windows#
This format, which has origins in the early collaborative work between Microsoft and IBM on the operating system OS/2, has become dominant on Windows platforms and is required for booting into all modern versions of Windows. NTFS had a big advantage over many file systems of its era because of to its journaling capabilities, including organizing data in complex ways and internally managing corruption issues.Īs Microsoft notes, the system also has a lot of other advantages, including the ability to handle large files and limit access controls to certain types of folders and files based on user permissions - a handy feature for system administrators. It was initially developed for Windows NT, the business-oriented operating system Microsoft first developed in 1993 that is the basis for all modern-day Windows versions.

NTFS is the primary file storage format for modern versions of Windows. REGISTER: Learn more about how data can power modern IT with the weekly CDW Tech Talk Series. Those factors offer different benefits, based on use case. This potentially makes file access faster by not requiring the disk to search for data, and means the layout of an NTFS drive can be more detailed and nuanced, whereas FAT32 maintains a more basic structure. NTFS, meanwhile, expands on the cluster idea by adding a file system called journaling, which effectively offers a script to record metadata onto the volume so changes can be tracked throughout the drive. With FAT, the disk manages data using a set of clusters based on a fixed-bit system, with FAT32 relying on a 32-bit structure.
Drive format that works for mac and windows fat how to#
A file system like NTFS or FAT works as something of a script for the computer to tell it how to manage data on a disk. Hard drives, on the other hand, run into issues with fragmentation over time, requiring the occasional defrag the added sophistication and speed of SSD and other types of flash storage, like USB drives, make this process largely unnecessary.įile systems act as a layer of data to manage the information on the disk. SSDs, for example, can extend their usable lifespan through a process called TRIM, which internally erases portions of the drive that are no longer in use. Hard drives, flash drives and solid-state devices (SSDs) rely on a variety of tactics to manage file storage, and these tactics often differ. Over time, different advantages for each file storage type have emerged, and both IT teams and end users will likely interact with each type - especially those who primarily use Microsoft Windows devices. Both were developed by Microsoft more than a quarter century ago and are heavily used in computing. Two of the most common formats are the New Technology File System (NTFS) and File Allocation Table (FAT), the latter most commonly seen as FAT32.
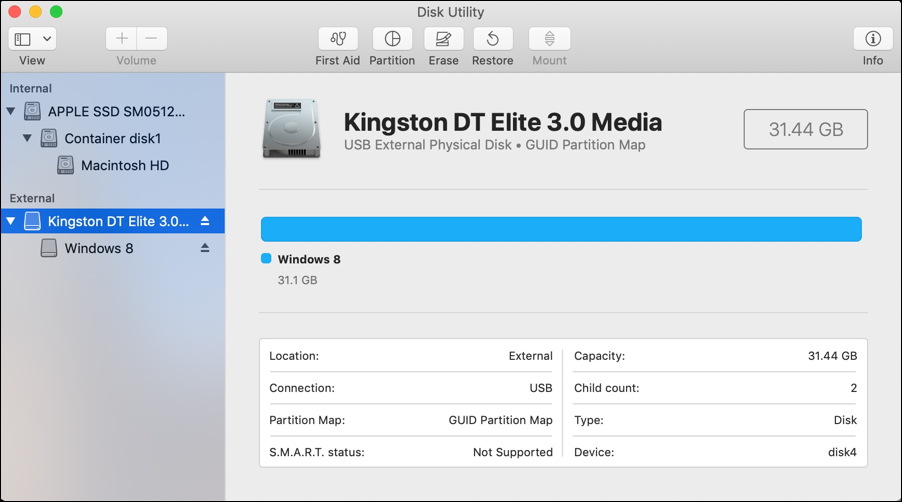
It may seem like a simple concept, but there are many ways to store files on a given device. With so many emerging technologies changing the way organizations do business, one of the most crucial digital tools is also one of the most basic: file storage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
